With the Hockey and Indoor Soccer seasons underway some may find themselves experiencing groin/medial thigh pain after putting your body through new demands with the start of the season.
GROIN STRAIN (ADDUCTOR STRAIN):
Cause:
An abrupt change in the muscle length/tone from overstriding, pivoting or a strong rapid contraction of the adductor group.
Sign and Symptoms:
Sudden sharp pain in the groin area, either in the belly of the muscle or higher at its insertion point. Swelling and bruising may present depending on the severity of the injury. Groin strains are graded 1, 2 or 3 depending on the extent of the injury.
If an acute sudden onset groin injury is not treated properly it is prone to recurring and causing long-term groin pain.
There are actually 5 muscles that make up your “groin” / adductor muscles; the pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, the gracilis and adductor magnus.
The main function of the adductors is to pull the legs back towards the midline, a movement called adduction. In the real world, they are used to stabilize and control the movement of the legs when running, walking, sprinting, playing football, horse riding, hurdling and any sport which requires fast changes in direction.
GROIN STRAIN TREATMENT
Treatment for a groin strain is based around immediate first aid to stop bleeding/bruising and swelling and then restoring the muscle to full function. The following can help with the treatment of groin muscle strains:
Proper Warm-up
Research shows that the best way to warm up muscles and tissue is through DYNAMIC activity. Which means; the old mentality of laying on the field or ice to stretch statically actually HINDERS the muscle performance and therefore does not benefit you at all.
Cold therapy
Immediate treatment for a suspected groin strain should be to apply cold therapy and compression as soon as possible to limit bleeding and swelling. The sooner a cold compress is applied to a strained groin the faster the rehabilitation process can begin.
Groin strapping
Taping or strapping the groin using elastic adhesive bandage can be done immediately after injury to provide support and compression to the injured muscle. It is also useful later in the rehabilitation program as an alternative to wearing groin support. Strapping will often provide more support than a groin wrap but will lose its effectiveness sooner as the tape stretches naturally.
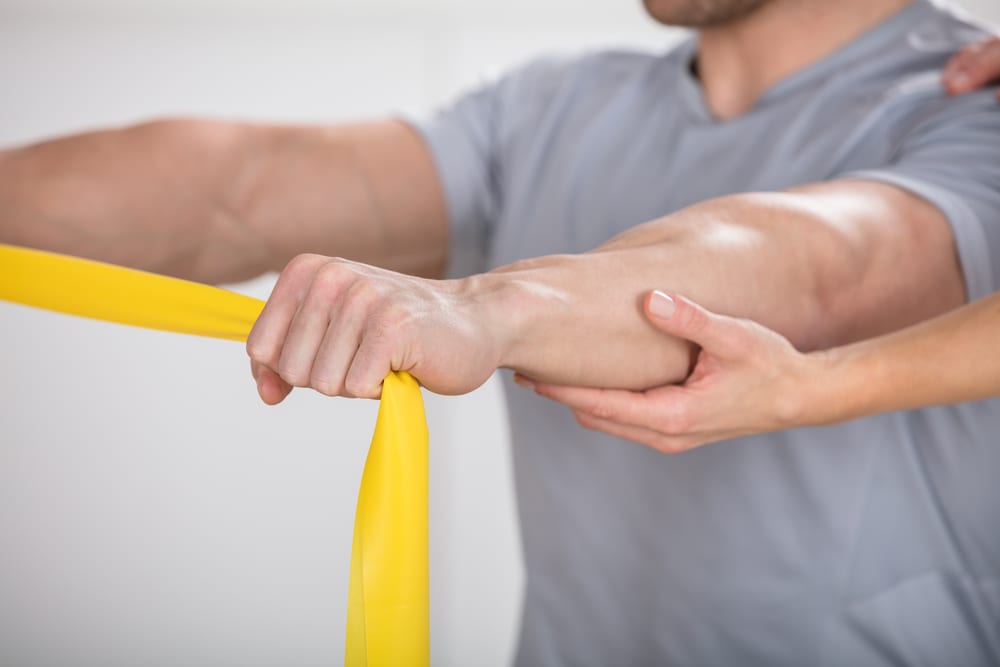
Strengthening exercises
The aim of strengthening exercises is to gradually increase the load through the muscles. Isometric or static exercises to start with progressing to dynamic exercises with a resistance band.
TIP: Eccentric loading, where the muscle group is resisted in a controlled lengthening fashion is key to avoiding any tendon-type injuries.
Soft Tissue Therapy and/or Acupuncture
By getting proper HANDS ON treatment to an injured muscle is imperative to the healing time frame and quality of healing of that particular tissue. Improving blood flow, breaking down scar tissue/adhesions and decreasing muscle hypertonicity are all key ingredients that will help for a proper and rapid recovery.
About Author
 Dr. Robert Garofalo
Dr. Robert Garofalo
Dr. Robert Garofalo graduated with clinic honours as a Doctor of Chiropractic at the Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College and has an Honours degree in Kinesiology from York University. He was a proud recipient of the Orthotic Group Excellence in Biomechanics Scholarship Award during his second year of study at the Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College. Dr. Garofalo is a certified Active Release Technique® provider, a certified Medical Acupuncture provider, and a certified Personal Trainer. During his final year at the Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College, Dr. Garofalo was the on-site athletic therapist for the Markham Waxers Junior “A” hockey club. He has always been involved in a variety of sports which fuels his passion for treating athletic-related injuries.


 Dr. Robert Garofalo
Dr. Robert Garofalo